If one of the couples has a dominant or recessive non-allelic genetic disease, the chance of giving birth to a child with the same genetic disease will be 1/2 or 1/4, such as hemophilia, spinocerebellar atrophy, achondroplasia, etc. By analyzing the cells of the embryos before implantation, PGT-M / PGD can separate out chromosomes that are attributable to the related genetic diseases and obviate the possibility of inheritance of the disease.
Thanks to the development of technology, PGT-M/PGD can aim at a specific known genetic disease in the family and can identify a non-allelic genetic disease in a rapid manner with an accuracy of as high as 90%. However, it cannot avoid chromosomal defects, congenital abnormalities, and other genetic diseases that have not been identified in the family. Therefore, after successful conception through IVF and PGT-M/PGD screening, the expectant mother still needs to receive prenatal checkups to ensure the health of the fetus.
service items
/genetic diagnosis/
Genetic Diagnosis
PGT-M / PGD
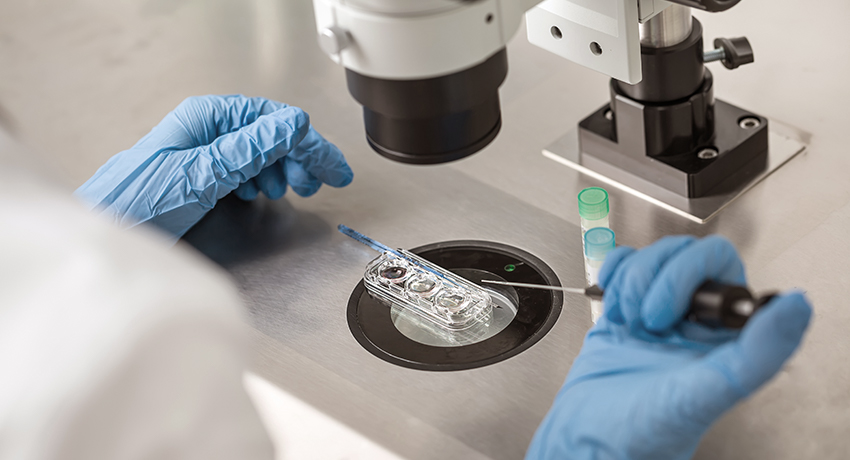

PGT-M / PGD
PGT-M / PGD
/Treatment process/
Detection process
01
/
Step01
Physician consultation
The doctors will determine whether PGT-M/PGD is suitable and required (a genetic diagnosis report and Family Tree will be required)
Step02
Fill in the documents
The doctor and the subject fill in the relevant documents
(The sample clearance process of the Ministry of Health and Welfare will last for 18 days)
(The sample clearance process of the Ministry of Health and Welfare will last for 18 days)
Step03
Cell sampling
Takes oral mucosa cell sample of the couple (and their parents/the child involved, etc.), it would take approximately 4 weeks to determine whether the test can be performed
Step04
IVF
IVF
Step05
Cell slice
Blastocyst stage embryo biopsy
Step06
Report released
The doctor implants the healthy embryo into the mother’s body based on the analysis report
Diagnosis report: E-mail/Fax
Diagnosis report: E-mail/Fax